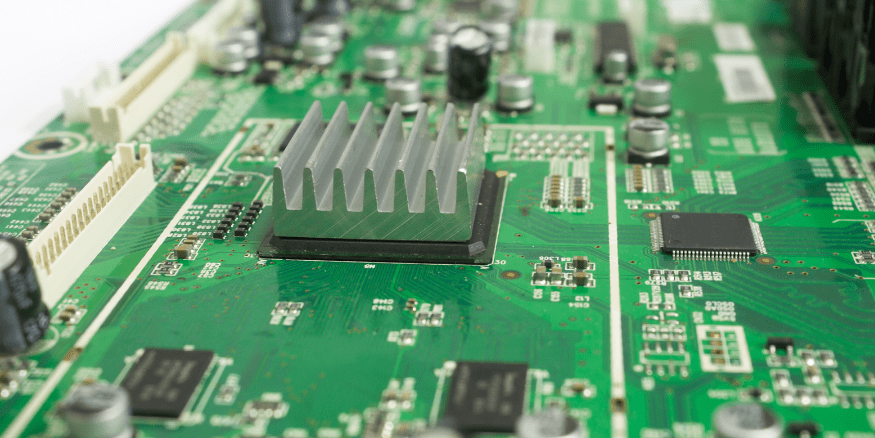
Maximize Heat Dissipation with the Bonded Fin Heat Sinks
We have seen a significant increase in the usage of electronic gadgets in our everyday lives as a result of technological improvement. One important feature of these gadgets that we frequently ignore is the amount of heat they produce when in use. If this heat is not properly controlled, it might seriously harm the gadget and possibly cause it to malfunction.
Heat sinks have developed into a crucial element in the design of electronic devices as a solution to this problem. This article will examine the advantages of one specific kind of heat sink, the Bonded Fin Heat Sink, for increasing heat dissipation in electrical equipment.
Heat dissipation is an essential consideration for electronic devices, as excessive heat can damage the device and its surrounding components. Use of heat sinks is one efficient method for removing heat from electrical equipment.
A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers heat from a heated item to a colder area. Among different types, bonded fin heat sinks are known for their high-performance cooling abilities. In this article, we will explore what heat sinks are and how they work to maximize heat dissipation.
What are Bonded Fin Heat Sinks?
Bonded fin heat sinks are a type of heat sink that consists of thin metal fins bonded to a base plate. The fins are typically made of aluminum or copper, which are good conductors of heat. The component that comes into touch with the hot object that has to be cooled is the base plate, which is likewise constructed of metal.
The increased surface area of the fins enhances the heat sink’s ability to dissipate heat. Electronic components like power amplifiers, CPUs, and GPUs that produce a lot of heat frequently employ bonded fin heat sinks.
How Do Bonded Fin Heat Sinks Work?
These heat sinks work based on the principle of convection, which is the transfer of heat from a hot object to a cooler environment through the movement of fluids. In the case of heat sinks, the fluid is air.
As heat is transferred from the base plate to the fins, the air surrounding them absorbs it and rises as a result. Cooler air replaces the heated air that is ascending and absorbs additional heat from the fins. As a result of this ongoing process, heat is continuously transferred from the hot object to the surroundings.
Increase the Surface Area of the Fins
The surface area of the fins is a critical factor in the heat dissipation performance of bonded fin heat sinks. More heat can be dispersed the more surface area there is. Hence, increasing the fins’ size or number can increase the heat sink’s ability to dissipate heat.
Optimize the Fin Spacing
The spacing between the fins is also an essential factor in the performance of heat sinks. The more closely together the fins are, the more surface area is available for heat dissipation. However, if the spacing is too close, it can hinder the flow of air between the fins, reducing the heat dissipation performance. Therefore, optimizing the fin spacing is crucial for maximizing heat dissipation.
Choose the Right Material
The material used for the base plate and fins is also critical in maximizing heat dissipation. Aluminum and copper are the most commonly used materials for bonded fin heat sinks because they are excellent conductors of heat. Although these materials come in many grades, some may have superior heat conductivity than others. As a result, choose the material with the best thermal conductivity can improve the heat sink’s capacity to disperse heat.
Use Thermal Interface Materials
Thermal interface materials are substances used to improve the thermal conductivity between two surfaces. With bonded fin heat sinks, a thermal interface material can be applied between the base plate and the hot object to improve heat transfer. Thermal interface materials are available in many of forms, including thermal grease, thermal pads, and phase-change materials.
Bonus Read
Electronic gadgets that produce a lot of heat may be effectively cooled down using bonded fin heat sinks. They are a preferred option for electrical designers and engineers because to their adaptable architecture, high-performance cooling capabilities, and affordability.
By expanding the fins’ surface area, adjusting their spacing, choosing the right material, and using thermal interface materials, heat sinks may effectively dissipate more heat.
As a consequence, electronic equipment operate better, are more dependable, and last longer. If you want to keep your electrical gadgets cool and operating at their best, bonded fin heat sinks are a great option.


